Overview of Industry 4.0 Technology
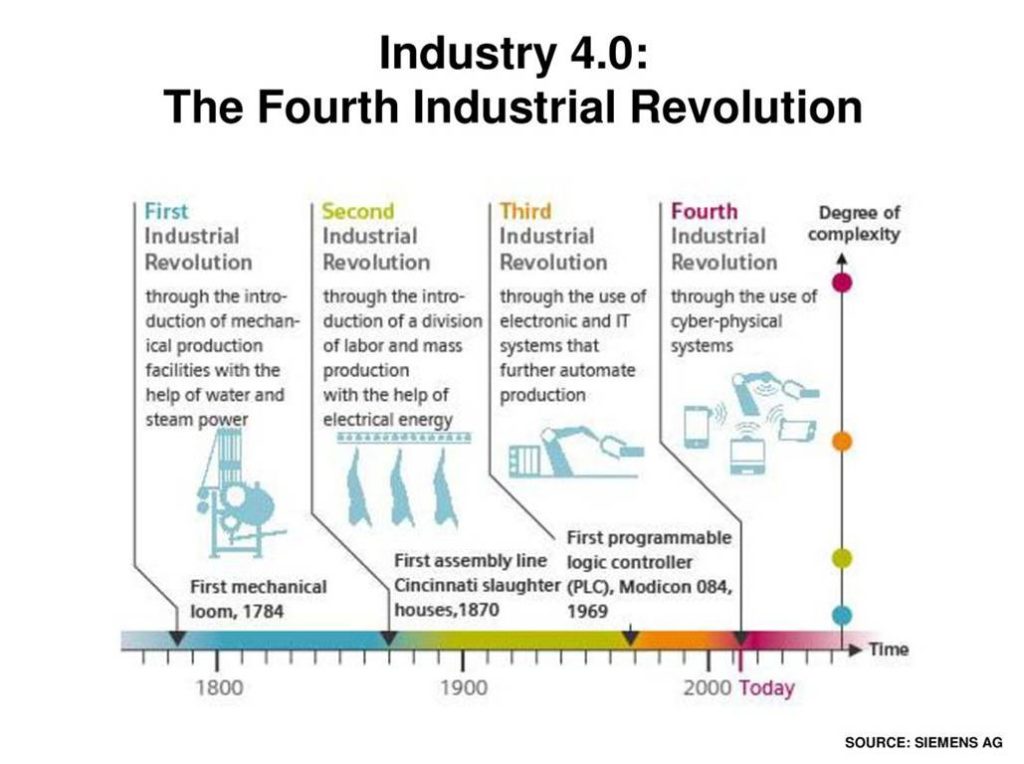
Industry 4.0 (the ‘fourth industrial revolution’) refers to the current trend of improved automation, machine-to-machine and human-to-machine communication, artificial intelligence, continued technological improvements and digitalization in manufacturing.
Industry 4.0 has been driven by 4 disruptors;
- a rise in data volumes
- computational power and connectivity
- emergence of analytics and business intelligence capabilities – e.g. new forms of human-machine interaction such as touch interfaces and augmented-reality systems
- improvements in transferring digital instructions to the physical world such as advanced robotics and 3D printing.
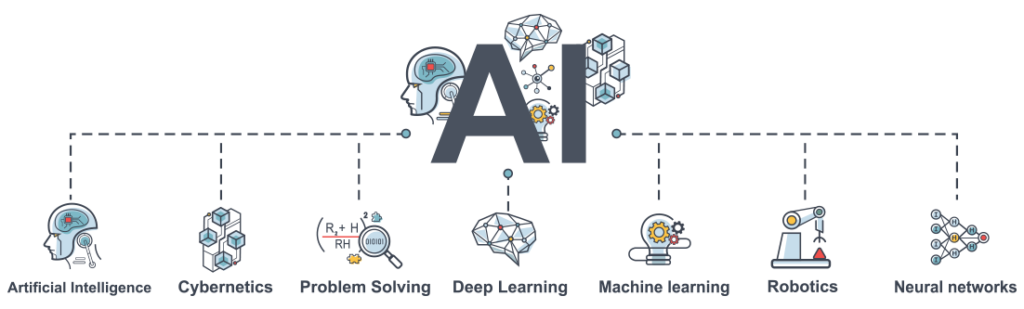
Artificial Intelligence within Industry 4.0
Artificial intelligence is no longer a vision for the future. Today, large data centers and enormous storage capacities make things possible that were believed for years to be distant concepts. Two branches of artificial intelligence, machine learning and deep learning, use the possibilities of big data to optimize processes, find new solutions, and gain new insights.
In a smart factory, production processes are connected – machines, interfaces, and components communicate with one another. Large amounts of data can be collected to optimize the manufacturing process. Big data supports process optimization by using image analysis and image recognition.
AI is Revolutionizing Manufacturing:
Following are the ways:-
- Smart Maintenance
- The rise of quality 4.0
- Human – Robot collaboration
- Making better products with generative designs
- Adapting to an ever changing market.
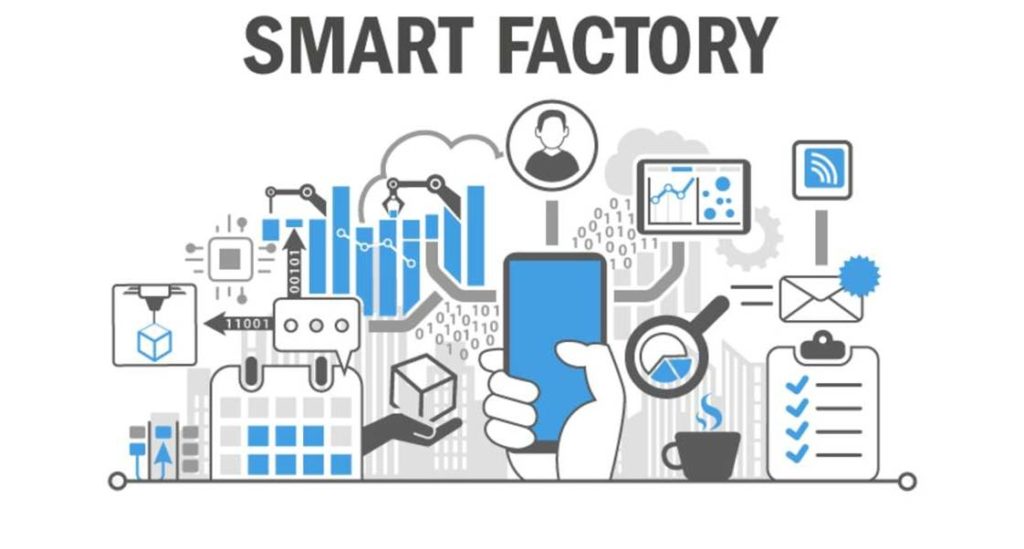
SMART FACTORY ( Another term for Industry 4.0):
The terms “Smart Factory,” “Smart Manufacturing,” “Intelligent Factory” and “Factory of the Future” all describe a vision of what industrial production will look like in the future.
In this vision, the Smart Factory will be much more intelligent, flexible and dynamic.
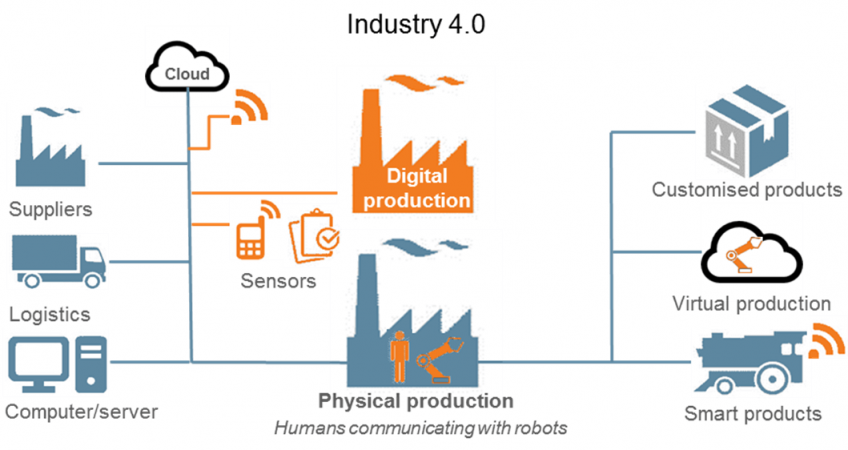
Manufacturing processes will be organised differently, with entire production chains – from suppliers to logistics to the life cycle management of a product – closely connected across corporate boundaries.
Individual production steps will be seamlessly connected.
The processes(Smart Factory) impacted will include:
- Factory and production planning.
- Product development.
- Logistics.
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP).
- Manufacturing execution systems (MES).
- Control technologies.
- Individual sensors and actuators in the field.
In a Smart Factory, machinery and equipment will have the ability to improve processes through self-optimisation and autonomous decision-making. This is in stark contrast to running fixed program operations, as is the case today.
INTERNET OF THINGS (IOT) WITHIN INDUSTRY 4.0
The concept of connecting any device with an on and off switch to the Internet (and/or to each other). This includes everything from cellphones, coffee makers, washing machines, headphones, lamps, wearable devices and almost anything else you can think of.
This also applies to components of machines, for example a jet engine of an airplane or the drill of an oil rig. If it has an on and off switch then chances are it can be a part of the IoT.
Applications Of IOT:
- Digital/Connected factory.
- Facility Management.
- Production Flow Monitoring.
- Inventory Management.
- Plant Safety And Security.
- Quality Control.
- Packaging Optimization.
- Logistics And Supply Chain Optimization.
CLOUD COMPUTING / TECHNOLOGY WITHIN INDUSTRY 4.0:
Cloud computing means storing and accessing data and programs over the Internet instead of your computer’s hard drive. The cloud is just a metaphor for the Internet.
- It has Less Operational Issues.
- It actually saves you Money.
- It requires less capital.
- It Increases collaboration amongst your Team.
- It Reduces your carbon Footprint.
- The cloud is always on.
- It gives employees a better work life balance.
- It has better security.
- It makes it easy to control your documents.
- It is easy to implement.