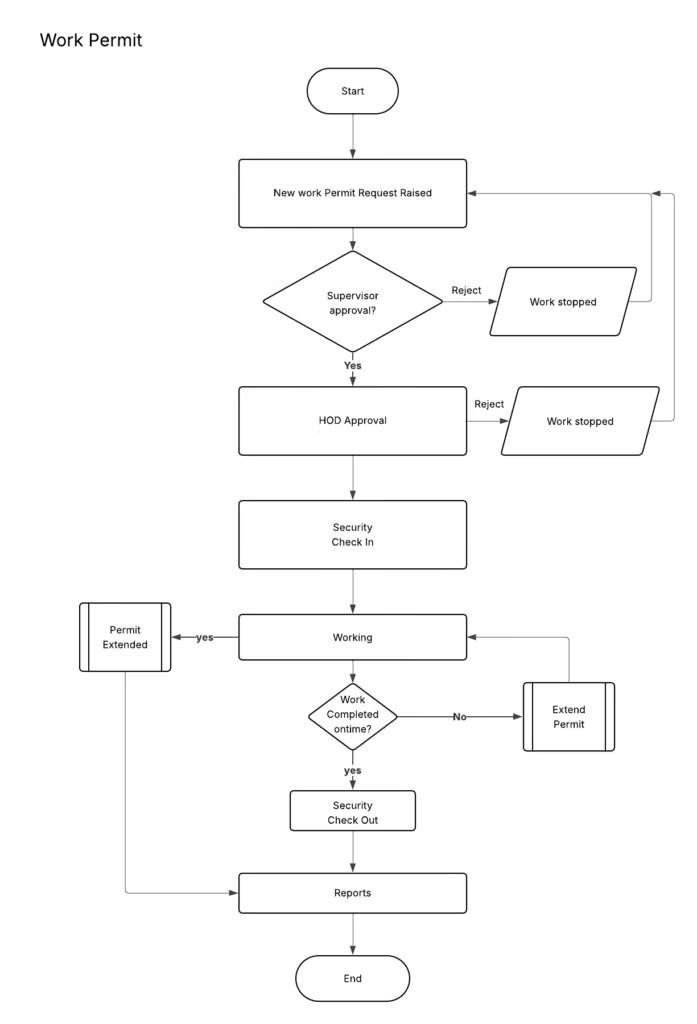
AI permit to work system for safety compliance:
Introduction
An AI Permit to Work (PTW) system is a smart digital solution that helps organizations manage high-risk work activities safely and in a controlled manner. Traditional PTW systems are often paper-based or manual, which can lead to delays, human errors, and missed safety checks. An AI-powered PTW system uses artificial intelligence to automate permit creation, risk checks, approvals, and monitoring. It ensures that all safety rules, procedures, and legal requirements are followed before work starts, during the job, and after completion. This makes workplaces safer and improves overall safety compliance.
Key Features of an AI-Based PTW System
An AI-based Permit to Work (PTW) system offers advanced features that help organizations manage high-risk work safely and efficiently. By using automation and intelligence, it ensures that all safety checks, approvals, and controls are completed correctly before work begins and throughout the job. These features reduce manual effort, improve safety compliance, and provide better visibility and control over work activities.
- Automated Permit Creation
The system automatically generates permits based on job type, location, and risk level, ensuring all required safety fields are completed correctly. - Intelligent Risk Assessment
AI identifies potential hazards using historical data, work conditions, and task details, and recommends suitable control measures before approval. - Digital Approval Workflow
Permits are routed digitally to the right supervisors and safety officers, reducing delays and speeding up approvals. - Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
The system tracks active permits and sends alerts for unsafe conditions, permit violations, or expired permits. - Centralized Dashboard and Reporting
Safety managers get a single dashboard to view all permits, ongoing work, risk status, and audit-ready reports for compliance checks.
Benefits of an AI Permit to Work System
An AI Permit to Work system offers a modern and efficient approach to managing high-risk work activities while ensuring strong safety compliance. By automating permit processes, risk assessments, and approvals, it reduces manual effort and human errors that are common in traditional systems. The system provides real-time visibility into ongoing work, identifies potential hazards early, and ensures all safety requirements are met before and during the job. Overall, an AI Permit to Work system helps organizations create safer workplaces, improve operational efficiency, and maintain consistent compliance with safety regulations.
- Improved Safety Compliance
AI PTW systems automatically check permits against safety standards, company policies, and legal requirements. This reduces the chance of missing critical safety steps and helps maintain full compliance. - Reduced Human Errors
Manual permits depend heavily on people, which can lead to mistakes. AI minimizes errors by validating data, identifying missing information, and flagging unsafe conditions in real time. - Faster Permit Approval Process
AI automates workflows and approvals, reducing delays. Permits can be reviewed and approved quickly, saving time while still maintaining safety. - Real-Time Risk Assessment
The system can analyse job risks using past data, site conditions, and work type. It alerts users about potential hazards and recommends safety controls before work begins. - Better Visibility and Control
Safety managers can see all active permits, ongoing jobs, and risk levels on a single dashboard. This improves decision-making and site control. - Audit-Ready Documentation
All permit data is stored digitally, making audits, inspections, and reporting easy. This helps organizations prove compliance during safety audits. - Cost and Time Savings
By preventing incidents, reducing downtime, and cutting paperwork, AI PTW systems help save operational costs and - improve productivity.
Use Case Tool:
| Safety Area | AI PTW Feature | How It Supports Safety | Compliance Alignment | Key Safety Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permit Authorization | AI-enabled permit creation and approval workflow | Ensures work begins only after meeting safety requirements | OSHA, ISO 45001 | Safe and controlled job execution |
| Hazard & Risk Control | AI-based hazard identification and risk scoring | Detects potential risks before issuing work permits | ISO 45001 | Reduced incident likelihood |
| Workforce & Contractor Safety | Mobile access to permits and safety instructions | Improves awareness of safety conditions at the worksite | Statutory safety laws | Higher compliance by workers |
| Permit Monitoring & Control | Real-time permit status and condition monitoring | Automatically pauses work when unsafe conditions arise | Audit and inspection standards | Continuous safety oversight |
| Audit & Accountability | Digital permit records with AI analytics | Provides traceable data for audits and investigations | Regulatory & management review | Strong safety governance |
Challenges:
Traditional Permit to Work (PTW) systems face several challenges that impact safety compliance and operational efficiency. Manual and paper-based processes often lead to human errors, incomplete permits, missed hazard identification, and inconsistent risk assessments. Permit approvals can be delayed due to the unavailability of supervisors, resulting in work stoppages. There is limited real-time visibility of ongoing high-risk activities, making it difficult for safety managers to monitor work and respond quickly to emergencies. Additionally, maintaining regulatory compliance and audit-ready documentation is difficult, as records may be misplaced, outdated, or non-standardized.
Solutions:
An AI-based Permit to Work system effectively overcomes these challenges by automating and digitizing the entire permit lifecycle. AI ensures all mandatory safety checks, hazards, and control measures are completed before approval, reducing errors and improving consistency. It intelligently identifies potential risks based on job type, location, and historical safety data, and speeds up approvals through digital workflows and instant notifications. Real-time dashboards provide full visibility of active permits and high-risk tasks, while built-in compliance rules and automatic audit trails help organizations meet safety standards such as ISO 45001 and OSHA, resulting in a safer, more proactive safety management system.

Conclusion:
An AI Permit to Work system plays a vital role in improving safety compliance and reducing workplace risks. By automating permit processes, identifying hazards in advance, and ensuring all safety checks are completed, it helps organizations prevent accidents and stay compliant with regulations. Overall, an AI-based PTW system creates a safer, more efficient, and well-controlled work environment.